Book a Consultation for Dermal Fillers with Dr. Laura Geige Today
Dermal Fillers for Ears: A Comprehensive Overview
Dermal fillers have become a popular and effective treatment option for individuals seeking to enhance the appearance of their ears. In the context of ear surgery, dermal fillers are used to address a range of concerns, from subtle enhancements to more significant corrections.
The use of dermal fillers in ear surgery is particularly useful for addressing asymmetries or imperfections in the ear shape, such as lop ear syndrome or microtia. Dermal fillers can help to create a more balanced and harmonious appearance by filling in indentations or hollows in the ear.
One of the most common applications of dermal fillers in ear surgery is for the treatment of ear asymmetry. In cases where one ear is significantly smaller or less prominent than the other, dermal fillers can be used to fill in the difference and create a more symmetrical appearance. This can involve using a single type of filler material or combining different materials to achieve the desired effect.
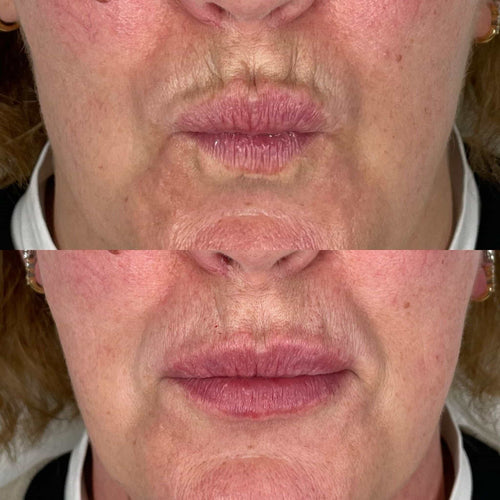
Dermal fillers are also used to correct congenital ear anomalies such as microtia, which is characterized by underdeveloped or partially developed ears. In these cases, dermal fillers can be used to augment the size and shape of the ear, creating a more balanced and natural appearance.
Another application of dermal fillers in ear surgery is for the treatment of ear cartilage defects or damage. In some cases, ear cartilage can become thin or fragmented due to injury, trauma, or other factors. Dermal fillers can be used to replace missing or damaged cartilage, restoring the ear’s natural shape and function.
When it comes to choosing the right dermal filler for ear surgery, several factors must be considered. The type of filler material used will depend on the individual’s specific needs and goals, as well as their overall health and medical history. Some common types of fillers used in ear surgery include hyaluronic acid (HA), calcium hydroxylapatite (CaHA), and poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA).
Hydroxyapatite fillers are often preferred for their ability to provide long-lasting results and their compatibility with a wide range of skin types. Calcium-based fillers, on the other hand, tend to be more absorbable and can provide shorter-term benefits.
Poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) is another popular choice for ear surgery due to its biocompatibility and ability to stimulate collagen production. This can lead to a more natural-looking result, as the body responds to the filler material by producing new tissue growth.
Before undergoing dermal filler treatment in ear surgery, it’s essential to consult with a qualified medical professional or board-certified plastic surgeon who has extensive experience in this area. During the initial consultation, the practitioner will assess the individual’s overall health and take careful measurements of their ears to determine the best course of treatment.
The procedure typically involves administering the dermal filler material directly into the affected area using a fine needle or cannula. The entire process can be completed in under an hour, and most patients report minimal discomfort or side effects during or after the treatment.
Aftercare for dermal filler treatment in ear surgery is relatively straightforward. Patients should follow their practitioner’s instructions for caring for the treated area, which typically involve gentle massage and maintenance injections to maintain optimal results.
Overall, dermal fillers have become a highly effective tool for enhancing the appearance of the ears during surgical procedures. By providing long-lasting solutions to common concerns such as asymmetry and imperfections, dermal fillers can help individuals achieve their desired aesthetic goals and enjoy a more confident smile.
Dermal fillers for *ears* have become an increasingly popular treatment option in the field of *_Otorhinolaryngology_*, as they offer a minimally invasive solution to improve the appearance of the ear. In this comprehensive overview, we will delve into the world of dermal fillers for ears, evaluating their safety and effectiveness based on recent studies.
Adermatoglycosides, also known as *_hyaluronic acid_* fillers, are the most commonly used type of dermal filler in ear procedures. These gel-like substances are composed of natural substances found in the body, making them a popular choice for individuals seeking a safe and effective treatment option.
The most well-known brand of *_hyaluronic acid_* filler for ear procedures is *_Restylane_*, which has been extensively studied and proven to be safe and effective. *_Restylane_* fillers are composed of _*nanocrystalline hyaluronic acid_* and are available in various concentrations.
Another type of dermal filler used in ear procedures is *_Calcium Hydroxylapatite_*, also known as *_Radiesse_*. These fillers contain tiny particles of calcium hydroxylapatite that stimulate the production of collagen, resulting in a more youthful appearance of the ears.
Dermal fillers for *_earlobe augmentation_* have gained significant attention in recent years. The goal of these procedures is to enhance the size and shape of the earlobe, often to balance out asymmetries or to create a more defined border between the earlobe and the ear canal. Studies have shown that dermal fillers can be an effective solution for earlobe augmentation, with results lasting up to 18 months.
Another area where dermal fillers are being used is in *_prominent earlobe deformities_*. These procedures involve injecting fillers into the affected areas to reshape and improve the appearance of the earlobe. Studies have demonstrated that dermal fillers can be a safe and effective solution for treating prominent earlobe deformities, with results lasting up to 24 months.
One of the primary benefits of using dermal fillers for *_ear procedures_* is their minimal invasiveness. Unlike traditional surgical procedures, which often involve making incisions or using scalpels, dermal filler injections are performed with a needle and can be completed in as little as 15-30 minutes.
Another advantage of dermal fillers is their reversibility. If an individual is not satisfied with the results of their procedure, it is possible to reverse the effects by dissolving the fillers using a special enzyme called hyaluronidase.
In terms of safety, dermal fillers for *_ear procedures_* have been extensively studied and proven to be safe when used properly. However, as with any medical treatment, there are potential risks associated with their use, including injection site reactions, swelling, and bruising.
It is essential to note that dermal fillers should only be administered by a qualified healthcare professional with experience in *_Otorhinolaryngology_* procedures. Inexperienced practitioners may increase the risk of complications or adverse reactions.
In conclusion, dermal fillers for *_ears_* offer a safe and effective solution for individuals seeking to improve the appearance of their earlobe or treat prominent earlobe deformities. By understanding the different types of fillers available, their benefits and risks, and the qualifications of practitioners who administer them, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Risks, Complications and Side Effects
Risks, complications, and side effects associated with ear dermal filler use are a crucial aspect to consider before undergoing treatment.
A thorough understanding of these potential issues can help you make an informed decision about your treatment plan.
Some common risks and complications associated with ear dermal fillers include:
- Infection: As with any injection, there is a risk of infection with ear dermal filler use. This can be treated with antibiotics.
- Allergic reactions: Some people may be allergic to the ingredients used in ear dermal fillers, which can cause symptoms such as redness, swelling, and itching.
- necrosis (death of skin cells): While rare, necrosis can occur if the filler material is injected too deeply or into a blood vessel.
- Scarring: In rare cases, scarring can occur at the injection site due to improper technique or infection.
- Sympathy ophthalmia (inflammation of both eyes): This rare complication can cause redness, swelling, and vision problems in one eye after treatment in the other eye.
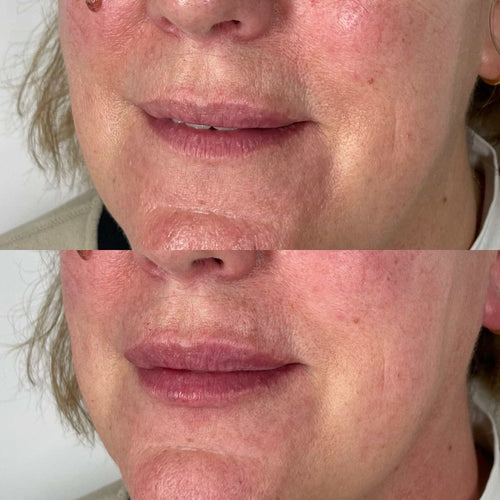
Common side effects of ear dermal fillers may include:
- Sensitivity or redness at the injection site
- Swelling or bruising around the treated area
- Mild pain or discomfort after treatment
- Itching or feeling of ticklishness in the treated area
- Temporary swelling of the eyelids, eyebrows, or facial muscles
More serious side effects can occur, including:
- Facial asymmetry (uneven appearance)
- Double vision or difficulty moving the eyes
- Sensory changes, such as numbness or tingling, in the face or ears
- Scarring or keloid formation at the injection site
In rare cases, ear dermal fillers can cause more severe complications, including:
- Permanent facial asymmetry
- Visual disturbances, such as blurred vision or loss of peripheral vision
- Pain or numbness in the face that persists after treatment has ended
It is essential to note that not all individuals will experience side effects or complications from ear dermal filler use. However, by understanding these potential risks and taking steps to minimize them, you can help ensure a safe and successful treatment outcome.
Dermal fillers are a common treatment option used during ear surgery, also known as otoplasty or ear reshaping surgery. While effective, these fillers can pose certain risks, complications, and side effects, as well as have specific precautions and contraindications that must be considered by patients before undergoing ear surgery with dermal fillers.
Risks associated with dermal fillers in ear surgery include infection, scarring, inflammation, and allergic reactions to the filler material. In rare cases, more serious complications such as nerve damage or vision problems can occur. The risk of complications is generally higher in patients with a weakened immune system or those who are taking immunosuppressive medications.
According to research studies published by the Mayo Clinic, the most common complication associated with dermal fillers used in ear surgery is granuloma formation. A granuloma is a localized inflammatory response that can occur at the injection site and may require surgical removal. Other complications include hematoma formation (bleeding) and filler migration or extrusion from the injection site.
Complications specific to ear surgery, such as temporary hearing loss or eardrum damage, are also possible with dermal fillers. However, these risks can be minimized by using only FDA-approved fillers and following proper pre- and post-operative care instructions provided by your surgeon.
Side effects of dermal fillers in ear surgery can range from mild to severe and may include redness, swelling, pain, itching, or bruising at the injection site. In some cases, patients may experience systemic side effects such as headaches, fatigue, or dizziness. Rarely, more serious side effects have been reported, including stroke, anaphylaxis, or filler-related respiratory problems.
Precautions that should be taken by patients before undergoing ear surgery with dermal fillers include stopping any medications that may affect bleeding or platelet function, such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Patients should also inform their surgeon of any previous surgical procedures or allergies they have.
Contraindications for using dermal fillers in ear surgery include patients with a weakened immune system, those taking immunosuppressive medications, and individuals with a history of bleeding disorders such as hemophilia. Additionally, patients with certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure or cardiovascular disease, should consult with their surgeon before undergoing ear surgery with dermal fillers.
Patients should also be aware that dermal fillers used in ear surgery are not suitable for everyone and may not provide the desired results for all patients. It is essential to discuss any concerns or questions you have with your surgeon before making a decision about using dermal fillers during your ear surgery procedure.
In summary, while dermal fillers can be a safe and effective treatment option for ear surgery, it is crucial to understand the potential risks, complications, side effects, precautions, and contraindications involved. By working closely with a qualified surgeon and following proper pre- and post-operative care instructions, you can minimize the risks associated with dermal filler use in ear surgery and achieve the desired results.
Dermal Fillers for Ears: A Balanced Approach from the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Foundation
Dermal fillers have become increasingly popular in recent years as a non-invasive treatment option to address various aesthetic concerns related to the ears.
These injectable fillers are made from biocompatible materials, such as hyaluronic acid, calcium hydroxylapatite, or poly-L-lactic acid, which are designed to mimic the natural structures found in the body.
The primary function of dermal fillers is to restore lost volume, smooth out wrinkles and folds, and enhance the overall appearance of the ears.
There are several types of dermal fillers that can be used for ear rejuvenation, including:
* Hyaluronic acid fillers (e.g., Restylane, Juvederm): These are popular choices due to their ease of use and versatility in addressing various concerns, from fine lines and wrinkles to volume loss.
* Calcium hydroxylapatite fillers (e.g., Radiesse): These fillers provide a more sustained result compared to hyaluronic acid fillers, making them suitable for more significant volume losses or structural defects.
* Poly-L-lactic acid fillers (e.g., Sculptra): These fillers are designed for longer-lasting results and are often used in conjunction with other treatments, such as blepharoplasty (eyelid surgery), to create a more harmonious facial balance.
When it comes to treating the ears, dermal fillers can be used to address various concerns, including:
* Earlobe sagging: Dermal fillers can help restore lost volume and achieve a more youthful appearance in the earlobe area.
* Tragus and anti-tragus folds: Filler injections can smooth out wrinkles and creases in these areas, creating a smoother silhouette.
Schedule Your Dermal Filler Appointment at It’s Me and You Clinic with Dr. Laura Geige
* Helix folds and protrusions: By injecting fillers into specific areas, it is possible to redefine the shape of the ear helix and create a more balanced appearance.
It is essential to note that dermal fillers for ears should be performed by an experienced and skilled healthcare professional or a board-certified ophthalmologist or otolaryngologist (ENT specialist) with extensive training in facial aesthetics.
The American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Foundation emphasizes the importance of careful patient selection, thorough pre-procedure evaluations, and meticulous injection techniques to achieve optimal results and minimize potential complications.
Long-term results from dermal filler use for ear rejuvenation can vary depending on factors such as the type of filler used, individual skin characteristics, and treatment frequency.
A study published in the Journal of Laryngology and Otology found that patients who received hyaluronic acid fillers experienced significant improvements in earlobe fullness and smoothness at 6 months post-injection, with results lasting up to 2 years.
Another study published in the same journal discovered that calcium hydroxylapatite fillers provided sustained results for ear helix folds and protrusions, with maintenance treatments needed every 12-18 months to maintain optimal aesthetic outcomes.
Ultimately, a balanced approach to dermal filler use for ears requires a comprehensive evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional, careful planning, precise execution, and regular follow-up appointments to ensure optimal results and address any concerns or complications that may arise over time.
The Journal of Laryngology and Otology experts emphasize the importance of maintaining realistic expectations, addressing individual patient needs, and prioritizing ongoing maintenance treatments to achieve long-lasting, natural-looking results.
Dermal fillers have become a popular non-surgical treatment option for individuals looking to enhance the appearance of their ears. The American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Foundation has published guidelines on the use of dermal fillers in the ear, emphasizing the importance of a balanced approach.
The foundation notes that dermal fillers can be used to correct certain conditions such as microtia, atresia, or helicotrachea ear deformities. Additionally, fillers can be utilized to enhance the shape and appearance of the ear cartilage, particularly for individuals with prominent antihelical folds or conchae.
There are various dermal fillers available on the market, including hyaluronic acid (HA), calcium hydroxylapatite (CAH), and poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA). Each type of filler has its own unique properties and indications. For example:
Book a Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige Now
- Hyaluronic acid fillers are commonly used for ear rejuvenation procedures due to their ability to mimic the natural moisture levels in the skin. They also tend to be less invasive and have a more predictable outcome compared to other fillers.
- Calcium hydroxylapatite fillers, on the other hand, provide a more long-lasting result and are often used for more complex ear deformities or surgical revisions.
- Poly-L-lactic acid fillers offer an even longer duration of action compared to CAH fillers and are also suitable for individuals with sensitive skin or allergies to other fillers.
It’s essential to note that not all dermal fillers are created equal, and the choice of filler ultimately depends on individual needs and preferences. A thorough consultation with a qualified healthcare professional or ear specialist is necessary to determine the most suitable filler for a specific condition or aesthetic goal.
Preparation is key to achieving optimal results with ear dermal fillers. Patients should follow these guidelines:
- Stop smoking at least two weeks prior to surgery, as smoking can impede healing and cause complications.
- Avoid blood thinners, such as aspirin or ibuprofen, for a specified period before the procedure.
- Avoid strenuous exercise or heavy lifting for several days following the treatment.
- Follow post-procedure instructions carefully to minimize swelling and promote optimal healing.
Post-operative care is also crucial in ensuring satisfaction with ear dermal fillers. Patients should:
Follow up with their healthcare provider or ear specialist as scheduled for post-procedure check-ups.
Attend follow-up appointments to ensure that the desired outcome has been achieved and make any necessary adjustments.
Address any concerns or complications promptly, such as swelling, redness, or unevenness.
Adequate follow-up care also involves monitoring for potential complications, including:
- Symmetrical swelling or bruising
- Asymmetry of the ear cartilage
- Changes in sensation or numbness
- Infection or abscesses
The American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Foundation emphasizes that proper post-procedure care and follow-up consultations are essential in minimizing complications and ensuring satisfaction with ear dermal fillers.
Read more about Kurious Kittens here. Read more about The Lady London here. Read more about Live Your Vows here. Read more about Azmia Magane here. Read more about Kindra Mann here. Read more about Carmen Alexandra here.
- NCTF 135 HA Near Send, Surrey - December 31, 2024
- Jaw Fillers For A Defined Jawline Near Dormansland, Surrey - December 16, 2024
- What Are Dermal Fillers For Ears? - December 12, 2024