Get Started with Dermal Fillers – Consult Dr. Laura Geige
Differences in Composition
Differentiating between Juvederm and Radiesse, two popular dermal fillers, requires an understanding of their distinct compositions and properties.
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a naturally occurring substance found in the body, particularly in connective tissue. It’s composed of molecules with varying molecular weights, ranging from 100 to 1 million kDa. Juvederm, manufactured by Allergan, utilizes this natural HA molecule, which accounts for its high viscosity and elasticity.
On the other hand, Calcium Hydroxylapatite (CaHA) is a synthetic filler composed of calcium, hydroxyl groups, and apatite crystalline structures. This unique composition gives CaHA a more rigid structure compared to HA, allowing it to maintain its shape longer.
A key difference between Juvederm and Radiesse lies in their molecular weights. Juvederm contains 5 molecular weight fractions of HA, with the highest fraction being above 1 million kDa, resulting in high viscosity and elasticity. Radiesse, on the other hand, has a uniform molecular weight, averaging around 500 kDa, which contributes to its more gel-like texture.
Another notable distinction between these two fillers is their stability over time. Juvederm’s HA molecules tend to break down faster compared to CaHA, with some studies suggesting that up to 20% of HA may degrade within the first year after treatment.
Radiesse, however, maintains its structure and calcium ion content for an extended period, often exhibiting minimal degradation over several years. This attribute is attributed to its unique mineral composition, which resists enzymatic breakdown by hyaluronidase enzymes naturally present in the body.
Furthermore, Juvederm has a more pronounced ability to integrate with surrounding tissue due to its HA content, allowing for more natural-looking results and better biocompatibility. In contrast, Radiesse’s CaHA can lead to more noticeable granulomas or calcifications, particularly around the injection site.
The choice between Juvederm and Radiesse largely depends on individual patient needs and treatment goals. For most patients seeking temporary fillers for lip augmentation, facial rejuvenation, or wrinkle correction, Juvederm’s HA-based composition is often preferred due to its fluidity and natural integration with tissue.
On the other hand, CaHA-based Radiesse might be a better option for individuals requiring more permanent results from dermal fillers, particularly in cases where significant volume loss or facial resurfacing are involved. However, patients must carefully weigh the trade-offs between Juvederm’s higher fluidity and Radiesse’s greater durability when choosing their preferred filler.
Hyaluronic acid-based fillers like Juvederm and Radiesse are both popular choices for facial rejuvenation, but they have distinct differences in terms of composition.
Juvederm is made from a nonsynthetic, naturally occurring substance called hyaluronic acid, which is found in the body. This acidic glycosaminoglycan (GAG) plays a crucial role in maintaining skin hydration and elasticity. In contrast, Radiesse is composed of a mixture of calcium hydroxylapatite and poly-L-lactic acid.
One key difference between Juvederm and Radiesse is the method of preparation. Hyaluronic acid used in Juvederm is derived from bacteria that are fermented to produce the substance, whereas Radiesse’s calcium hydroxylapatite is obtained through a process of mineral extraction from limestone.
Another significant difference lies in their longevity. Juvederm fillers typically last anywhere from six months to one year, depending on the individual and the area treated. In contrast, Radiesse fillers can last up to two years or more due to their unique calcium hydroxylapatite composition that is slowly absorbed by the body.
From a clinical perspective, Juvederm is often preferred for facial augmentation due to its smooth, gel-like texture and excellent biocompatibility. This makes it an ideal choice for soft tissue fillers like lips, cheeks, and nasolabial folds.
Radiesse, on the other hand, is often favored for deeper injections such as cheek hollows or lip lines where a more substantial amount of volume is needed. Its unique texture also allows it to provide a more natural-looking contour.
It’s worth noting that Radiesse requires a separate injection process compared to Juvederm, which can be more time-consuming and may require multiple sessions.
In terms of downtime, both fillers have similar recovery profiles. Mild bruising, swelling, and redness are common side effects, but they typically subside within a few days.
Ultimately, the choice between Juvederm and Radiesse depends on individual skin type, desired results, and personal preference. A thorough consultation with a qualified dermatologist or plastic surgeon is essential to determine which filler best suits your unique needs.
Hyaluronic acid (HA) and calcium hydroxylapatite (CaHa) are two popular dermal fillers used for various cosmetic procedures, including facial rejuvenation. While both have gained widespread acceptance in the medical community, their differences in composition, properties, and effects on the skin make them suitable for different individuals.
Research suggests that hyaluronic acid is more closely related to the skin’s natural substances, making it a popular choice for many patients. HA is a naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan (GAG) found in the body, particularly in connective tissue. Its composition and structure are similar to those of human skin, making it an ideal candidate for dermal fillers.
On the other hand, calcium hydroxylapatite, the primary component of Radiesse, is a synthetic, bioactive glass-like material that has been engineered to mimic the inorganic components of natural bone tissue. While CaHa has its own set of advantages, it differs significantly from HA in terms of composition and properties.
The key differences between Hyaluronic Acid and Calcium Hydroxylapatite are as follows:
- Composition: HA is a natural GAG, while CaHa is a synthetic, bioactive glass-like material.
- Molecular structure: The molecular structure of HA is hydrophilic and has a high degree of water retention, whereas CaHa is more hydrophobic and has a lower water-holding capacity.
- Viscosity and flowability: HA fillers tend to have a higher viscosity than CaHa fillers, which affects their ability to flow through small incisions.
- Durability and longevity: HA fillers typically last for 6-12 months, whereas CaHa fillers can provide longer-lasting results, often up to 18-24 months or more in some cases.
- Biocompatibility and safety profile: Both HA and CaHa are generally well-tolerated, but individual reactions to these fillers can vary. Some patients may experience inflammation, redness, or swelling at the injection site.
- Cost-effectiveness: HA fillers tend to be less expensive than CaHa fillers, especially for smaller treatment areas.
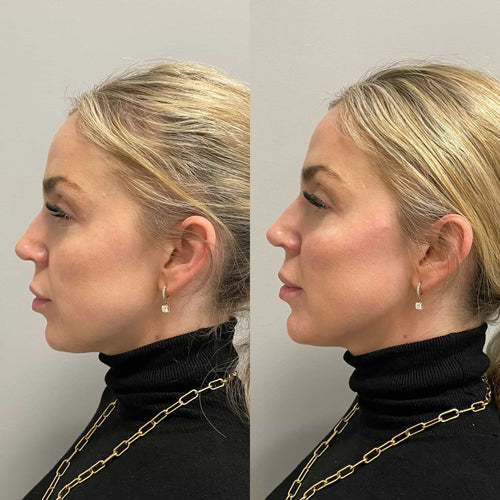
In summary, while both Hyaluronic Acid and Calcium Hydroxylapatite have their strengths and weaknesses, the differences in composition, properties, and effects on the skin make one more suitable for certain individuals. Hyaluronic acid is a popular choice due to its natural relationship with the skin’s substances, making it an attractive option for patients seeking a minimally invasive treatment.
Differences in composition between Juvederm and Radiesse are a crucial factor to consider when deciding which one is better for your specific needs.
Juvederm contains hyaluronic acid, a naturally occurring substance found in the body that provides moisture, hydration, and structure to facial tissues. This makes it an excellent choice for treating mild to moderate lines, wrinkles, and lips.
Radiesse, on the other hand, contains calcium hydroxylapatite, a synthetic material derived from minerals. While this may seem intimidating, Radiesse’s unique composition allows it to provide more robust results for deeper lines and wrinkles that require more structural support.
The key difference between hyaluronic acid and calcium hydroxylapatite is their interaction with the body. Hyaluronic acid is absorbed by the body over time, making it less long-lasting compared to Radiesse’s synthetic material.
Radiesse’s calcium hydroxylapatite particles can last up to two years in the body, providing a more sustained effect that is often necessary for correcting deeper wrinkles and fine lines. In contrast, Juvederm’s effects typically last between six months to one year.
Another difference in composition lies in the way each product interacts with collagen production in the skin. Hyaluronic acid stimulates collagen production, which can lead to a more natural-looking result as the body absorbs the filler material and responds by producing new collagen fibers.
Radiesse, however, does not stimulate collagen production. Instead, it works by providing immediate structural support, allowing for faster results. This is particularly beneficial for patients with severe scarring or irregular skin texture.
It’s essential to consider your individual skin concerns and needs when choosing between Juvederm and Radiesse. If you’re looking for a more natural-looking result that addresses mild to moderate lines and wrinkles, hyaluronic acid-based fillers like Juvederm may be the better choice.
However, if you’re dealing with deeper, more pronounced lines and wrinkles that require robust structural support, Radiesse’s synthetic material and longer-lasting effects make it a more suitable option.
Ultimately, the decision between Juvederm and Radiesse depends on your unique skin concerns, treatment goals, and personal preferences. Consultation with a qualified healthcare professional can help determine which product is best suited for your individual needs.
Efficacy and Durability
Durability is a crucial factor to consider when choosing between Juvederm and Radiesse for dermal filler treatments. While both products can provide long-lasting results, Juvederm has gained a reputation for its superior durability due to its unique formulation.
Juvederm’s durability is attributed to its hyaluronic acid composition, which allows it to integrate with the body’s natural collagen and elastin fibers. This integration helps the filler to last longer, reducing the need for frequent touch-ups or revisions.
Radiesse, on the other hand, uses a calcium hydroxylapatite (CaHA) microsphere technology to provide a more gradual and sustained release of filler material. While this can be beneficial for some patients, it may not offer the same level of durability as Juvederm in terms of overall longevity.
Results from Radiesse often start to degrade within 6-12 months, whereas Juvederm’s results can last up to 2 years or more with proper aftercare and maintenance. However, individual patient outcomes may vary depending on factors such as facial anatomy, lifestyle habits, and individual healing processes.
One key area where Radiesse excels is in its ability to provide immediate gratification for patients seeking dramatic, sculptural results. The CaHA microspheres are larger than those used in Juvederm, allowing for a more dramatic transformation in just one treatment session.
However, this trade-off comes with a potential drawback: Radiesse may require more frequent maintenance treatments to maintain the desired level of correction. This is particularly relevant for patients seeking long-term, sustained results from dermal fillers.
In terms of reversibility, both Juvederm and Radiesse are considered relatively safe and reversible. However, some patients may experience complications or adverse reactions that can lead to irreversible outcomes, such as granulomas, necrosis, or scarring.
Granulomas, in particular, have been associated with Radiesse use, although this is an extremely rare complication. In the event of a granuloma forming beneath the skin’s surface, treatment options may be limited to surgical excision or injection of dissolvable materials like hyaluronidase.
By contrast, Juvederm has a generally good safety profile and is less likely to cause complications that lead to irreversible outcomes. However, individual patient factors such as pre-existing medical conditions, allergies, or medications can influence the risk of adverse reactions.
Ultimately, the choice between Juvederm and Radiesse for dermal filler treatments depends on a patient’s unique needs, preferences, and goals. A consultation with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist is essential to determine which product best suits each individual’s requirements.
The importance of proper aftercare and maintenance cannot be overstated, regardless of the chosen product. This includes adhering to post-procedure instructions, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and scheduling follow-up appointments as recommended by the practitioner.
Juvederm and Radiesse are two popular dermal fillers used to treat various facial wrinkles and folds. While both products have their own set of benefits, efficacy and durability are crucial factors to consider when choosing between them.
Studies have shown that Juvederm can provide lasting results, with some patients experiencing effects lasting up to two years. This is due to its unique composition, which includes hyaluronic acid, a naturally occurring substance found in the body. The hyaluronic acid in Juvederm helps to maintain its structure and elasticity, leading to more sustained results.
Radiesse, on the other hand, is also effective but may not provide the same level of durability as Juvederm. Radiesse contains calcium hydroxylapatite, a biocompatible material that is slowly absorbed by the body over time. While this can lead to a natural-looking result, it may require more frequent touch-ups compared to Juvederm.
- One key factor contributing to Juvederm’s durability is its ability to be replenished from within the body.
- Another advantage of Juvederm is its flexibility, allowing it to adapt to changes in facial structure and expression.
It’s worth noting that individual results may vary, and factors such as skin type, facial structure, and treatment technique can influence the longevity of the results. Additionally, maintenance treatments may be necessary to maintain optimal results with either product.
Durability is also influenced by proper aftercare and post-treatment instructions. Patients who follow a consistent skincare routine, avoid sun exposure, and use recommended products can help extend the lifespan of their treatment results.
Ultimately, the decision between Juvederm and Radiesse depends on individual preferences and needs. Those seeking more long-lasting results may prefer Juvederm, while others may opt for Radiesse based on its unique characteristics and benefits.
In conclusion, both Juvederm and Radiesse are effective dermal fillers with distinct advantages and disadvantages. When considering which product is better suited to their needs, patients should weigh the potential benefits and drawbacks of each option carefully.
Efficacy and Durability are two crucial factors to consider when evaluating the effectiveness of a dermal filler, such as Juvederm or Radiesse.
Both Juvederm and Radiesse are widely used for various cosmetic procedures, including facial rejuvenation, lip augmentation, and wrinkle treatment. While both products have their own strengths, understanding their efficacy and durability is essential to make an informed decision.
- Efficacy refers to the product’s ability to deliver the desired results, which in this case, is the restoration of lost volume, elasticity, or firmness to the skin.
- Durability, on the other hand, refers to how long the results last. This is critical in maintaining the effectiveness of the treatment over time.
Radiesse stands out for its ability to provide instant results, thanks to its unique calcium-based formula that immediately stimulates collagen production and provides volume replenishment. However, Radiesse may require multiple injections to achieve the desired effect, as it is not as potent as Juvederm in terms of fillers per syringe.
One major advantage of Radiesse is its long-lasting results, with some patients experiencing effects that can last up to 18 months or more. This prolonged duration of action allows for fewer touch-ups and a more satisfying overall outcome.
Juvederm, on the other hand, has become known for its flexibility in terms of application. It comes in various formulas (e.g., Ultra, Volbella, and Voluma) each with specific uses and applications. This versatility makes Juvederm an ideal choice for a wide range of facial rejuvenation treatments.
Moreover, Juvederm results tend to last around 6-12 months, although this can vary depending on individual factors such as lifestyle, skin type, and treatment area. While fewer injections are required with Juvederm compared to Radiesse, its shorter duration may necessitate more frequent follow-up treatments.
To illustrate the difference between these two fillers in terms of efficacy and durability, here’s a comparison based on user experiences and reviews:
- Radiesse: Provides immediate results due to its fast-acting formula. However, it may require multiple injections, as mentioned earlier. Long-lasting effects are reported by many users, with some achieving results lasting up to 18 months.
- Juvederm: Offers versatility in terms of application and formulators. Results tend to last around 6-12 months, depending on individual factors. Users often praise Juvederm’s flexibility and ease of use.
In conclusion, both Radiesse and Juvederm are effective dermal fillers that deliver excellent results for their respective strengths. While Radiesse excels in terms of long-lasting effects, Juvederm’s versatility and adaptability make it an ideal choice for a broader range of treatments and patient needs.
Efficacy and Durability are crucial factors to consider when choosing a dermal filler, particularly when deciding between Juvederm and Radiesse.
In terms of reversibility, hyaluronic acid fillers like Juvederm are generally considered more easily reversible than calcium hydroxylapatite fillers.
This is because hyaluronic acid fillers can be dissolved with the addition of a specific enzyme called hyaluronidase, which breaks down the filler material. This reversibility makes hyaluronic acid fillers such as Juvederm a popular choice for those who want to maintain the flexibility to change their minds or try out different facial expressions without long-term commitment.
In contrast, calcium hydroxylapatite fillers, like Radiesse, are less easily reversible. These fillers require surgical excision or injection dissolution methods to remove excess material, which can be more invasive and carries a higher risk of complications.
Some key differences in terms of reversibility between hyaluronic acid fillers (like Juvederm) and calcium hydroxylapatite fillers (like Radiesse) include:
- Hyaluronic Acid Fills: Generally, reversible with enzyme dissolution; less risk of complications compared to surgical excision or injection dissolution methods.
- Calcium Hydroxylapatite Fills: Less reversible, requiring more invasive removal methods (surgical excision or injection dissolution); higher risk of complications.
Another important consideration is the duration of results. Both types of fillers offer varying durations of efficacy, with some lasting up to a year and others for several months.
Juvederm fillers generally provide longer-lasting results compared to Radiesse fillers, making them suitable for those who want a more durable solution. However, both types of fillers require regular maintenance treatments to maintain optimal effects.
The duration and reversibility of these fillers can be influenced by factors such as:
•Filler material
•Individual skin type
•Application technique
•Skin care habits
Ultimately, the decision between Juvederm and Radiesse comes down to individual preferences and needs. While hyaluronic acid fillers offer greater reversibility, calcium hydroxylapatite fillers provide more durable results.
Side Effects and Risks
– Both Juvederm and Radiesse are popular dermal fillers used to address various facial concerns, such as fine lines, wrinkles, and lip augmentation. However, each has its unique properties, indications, and potential side effects.
– Common Side Effects:
- Temporary redness, swelling, or bruising at the injection site
- Pain or stinging sensation during or after the procedure
- Itching or burning sensations in some cases
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Fever
- Mild headaches or dizziness
– Rare but Serious Complications:
- Anaphylaxis: a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction
- Eye problems, including dry eye, vision changes, or eyelid swelling
- Infected wounds or nodules at the injection site
- Nerve damage, leading to numbness or loss of sensation
- Scarring or lumps under the skin
- Allergic reactions to the filler itself or to the lidocaine used during the procedure
– Specific Risks Associated with Juvederm:
- Potential for a “mask-like” appearance if too much product is injected, causing unevenness in facial features
- Increased risk of bruising or swelling when combining multiple areas treated simultaneously
– Specific Risks Associated with Radiesse:
- Potential for a more noticeable “mask-like” appearance if too much product is injected, leading to uneven facial contours
- Increased risk of lumps or nodules under the skin due to the calcium hydroxylapatite particles used in the filler
- Potential for delayed swelling or redness at the injection site
Get a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
– Long-term Risks:
- Long-term effects of fillers on facial structure and overall appearance, including potential changes to skin elasticity or firmness
- Potential for fillers to break down over time, requiring touch-ups or replacement procedures
- Systemic reactions, such as autoimmune responses or inflammatory conditions, in rare cases
– To minimize the risks associated with dermal fillers like Juvederm and Radiesse, it is essential to choose a qualified practitioner with extensive experience in their use. This includes following proper pre- and post-treatment guidelines, selecting the appropriate filler for your individual needs, and being aware of potential complications that may arise.
Juvederm and Radiesse are two popular dermal fillers used for various cosmetic procedures to rejuvenate the face. While both fillers can produce excellent results, it’s essential to be aware of their potential side effects and risks.
- Bruising: Swelling, redness, and bruising are common side effects associated with both Juvederm and Radiesse. These symptoms usually resolve on their own within a few days but can take up to two weeks in some cases.
- Swelling: Temporary swelling at the injection site is another possible side effect of both fillers. This discomfort can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers or cold compresses.
- Redness: Redness and inflammation are common reactions to both Juvederm and Radiesse. In most cases, this subsides within a few days but may persist for up to two weeks in some individuals.
Other less common side effects of both fillers include:
- Nasal congestion: Temporary nasal blockage or congestion can occur due to swelling around the nose and sinuses.
- Sense of pressure: Some patients may experience a sense of pressure in their face, especially after Radiesse treatment.
- Itching or burning sensation: Mild itching or a burning feeling at the injection site is rare but can occur with both fillers.
- Allergic reactions: Although rare, some individuals may be allergic to one or both of the fillers. Symptoms include hives, swelling, and difficulty breathing.
Radiesse carries an additional risk of complications due to its unique calcium hydroxylapatite structure. These can include:
- Foreign body reaction: In rare cases, the body may react to Radiesse as a foreign substance, leading to swelling, redness, or abscesses.
- Painful lump formation: Some patients have reported forming painful lumps at the injection site after Radiesse treatment.
- Difficulty swallowing: Due to its dense structure, Radiesse can cause difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) in some cases.
Book a Consultation for Dermal Fillers with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
It’s essential for individuals considering Juvederm or Radiesse treatments to discuss their medical history and potential risks with a qualified healthcare professional. By understanding these side effects and risks, patients can make an informed decision about which dermal filler is best suited for their individual needs and concerns.
Radiesse is a dermal filler made from radiances calcium hydroxylapatite, a type of collagen that provides volume and structure to the skin.
The benefits of Radiesse include its ability to stimulate collagen production, which can lead to longer-lasting results compared to some other fillers. Additionally, it has been shown to be effective in treating a range of cosmetic concerns, including nasolabial folds, marionette lines, and lip augmentation.
However, as with any medical treatment, there are potential side effects and risks associated with Radiesse.
Rare but potentially serious complications have included granulomas, which are clusters of inflammatory cells that can cause redness, swelling, and scarring. In rare cases, these granulomas can be large enough to disfigure the treated area.
Infection is another potential risk associated with Radiesse, although this is extremely rare. According to FDA reports, there have been isolated cases of infection at the injection site following Radiesse treatment.
Other possible side effects of Radiesse may include redness, swelling, bruising, and itching at the injection site. These symptoms are usually mild and temporary, but can be uncomfortable for some individuals.
Pain or tenderness at the injection site is also a potential side effect of Radiesse, although this is typically short-lived.
It’s worth noting that while granulomas and infection are rare complications associated with Radiesse, they are serious concerns that can have long-lasting effects on the appearance of the skin. If you’re considering Radiesse for cosmetic treatment, it’s essential to discuss these risks with your healthcare provider in detail.
When comparing Radiesse to Juvederm, it’s also worth considering other factors such as the type of filler material used, the expected duration of results, and any specific concerns or needs you may have as an individual. Ultimately, the choice between Radiesse and Juvederm will depend on your unique goals, skin type, and medical history.
In general, Juvederm is a more commonly used and well-established filler, with a broader range of approved uses and longer-term results. However, it’s also been linked to rare complications such as nodules, lumps, and infection.
To minimize the risk of complications associated with any dermal filler, including Radiesse and Juvederm, it’s essential to follow pre- and post-treatment instructions carefully, choose a qualified and experienced healthcare provider, and have realistic expectations about the results.
By being informed and taking a cautious approach to dermal filler treatment, you can help ensure a safe and successful outcome that meets your cosmetic goals.
Discussing potential side effects and risks with a dermatologist before undergoing treatment is crucial when considering dermal fillers like Juvederm and Radiesse.
The American Academy of Dermatology emphasizes the importance of thorough evaluation and discussion between patients and their dermatologists to ensure informed decision-making.
Common side effects of dermal fillers include:
-
Redness and swelling at the injection site
-
Pain, bruising, or numbness at the injection site (rare)
-
Itching, burning, or stinging sensations during treatment (usually temporary)
Risks associated with dermal fillers include:
-
Infection at the injection site (rare but possible)
-
Allergic reactions to the filler material or preservatives (extremely rare but possible)
-
Granulomas, which are small, localized inflammation caused by an immune response to the filler (rare but possible)
-
Permanent scarring, although this is extremely rare
In the context of Juvederm and Radiesse, some specific considerations arise:
Juvederm contains hyaluronic acid, a naturally occurring substance in the body. This reduces the risk of an allergic reaction compared to other fillers.
Radiesse, on the other hand, contains calcium hydroxylapatite, which is made from minerals found in the human body. However, some patients may be allergic to these minerals.
Both Juvederm and Radiesse are generally well-tolerated, but as with any medical treatment, there are potential risks and side effects that need to be discussed with a dermatologist before making a decision.
A thorough discussion with a dermatologist will help determine which filler is best suited for your individual needs, skin type, and concerns. This ensures you have a clear understanding of the benefits and risks involved.
Read more about Cycle for Azaylia here. Read more about Pinnacle Wellbeing Media here. Read more about Carmen Alexandra here. Read more about Pinnacle Wellbeing Media here.
- JCPenney Associate Kiosk Login, JCP Kiosk Schedule, Features, And Benefits - May 16, 2025
- Sculptra Surrey – Collagen Stimulation Therapy Near Busbridge, Surrey - January 5, 2025
- Nasolabial Fold Fillers – Marionette Lines Near Farleigh, Surrey - December 19, 2024